Section: New Results
Learning brain regions via large-scale online structured sparse dictionary-learning
We propose a multivariate online dictionary-learning method for obtaining de-compositions of brain images with structured and sparse components (aka atoms). Sparsity is to be understood in the usual sense: the dictionary atoms are constrained to contain mostly zeros. This is imposed via an 1-norm constraint. By "struc-tured", we mean that the atoms are piece-wise smooth and compact, thus making up blobs, as opposed to scattered patterns of activation. We propose to use a Sobolev (Laplacian) penalty to impose this type of structure. Combining the two penalties, we obtain decompositions that properly delineate brain structures from functional images. This non-trivially extends the online dictionary-learning work of Mairal et al. (2010), at the price of only a factor of 2 or 3 on the overall running time. Just like the Mairal et al. (2010) reference method, the online nature of our proposed algorithm allows it to scale to arbitrarily sized datasets. Experiments on brain data show that our proposed method extracts structured and denoised dictionaries that are more intepretable and better capture inter-subject variability in small medium, and large-scale regimes alike, compared to state-of-the-art models.
|
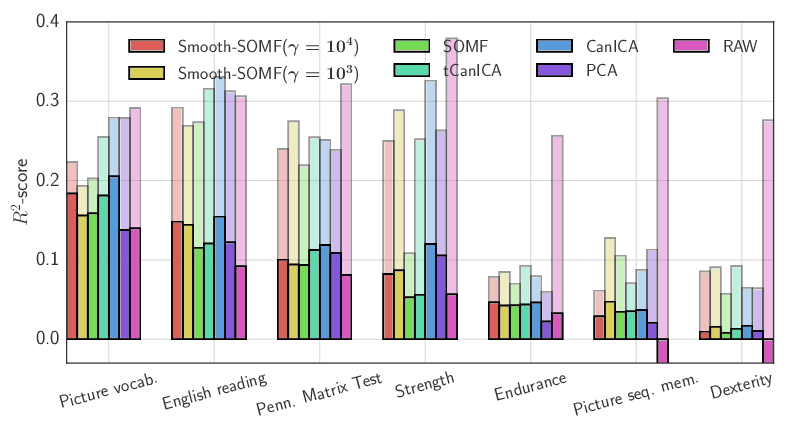
See Fig. 4 for an illustration and [19] for more information.